The battle of chips, an inch of land...

Rivers and mountains only linger in my dreams.
The motherland has not been close for many years.
But it can't be changed in any way.
My Chinese Heart
......
Thirty-nine years ago, the song "My Chinese Heart" written by Master Huang Zhan is still a classic, but recently the land that once praised the "Yangtze River, the Great Wall, Huangshan Mountain and the Yellow River" has become a mess because of a bunch of "waste green.
We can't help asking: dresses are often, oh no, it should be Zeng. Is the heart they wore in dresses still a Chinese heart?
Of course, we must be aware that these waste youths are a group of "thugs" who dare not even show their faces. They do not represent the majority or anyone; they are just a group of people who are manipulated by "willing people" and live in foreign media. "Poor people" in the black and white ".
As for the attitude of the mainland, it is not so much anger as disappointment; it is like a mother facing the unreasonable behavior of Xiong Haizi.
What was Hong Kong's status, the absolute center of economy and entertainment? But what is Hong Kong now?
Don't talk about Hollywood in the film and television industry. Even Bollywood can't match it. The once shining Hong Kong stars are also blue and yellow. Only Gu Tianle, Andy Lau, Zhang Jiahui and others are "dead".
In terms of economy, as the center of the third industrial transfer of the industrial revolution, the "four little dragons of Asia": South Korea has become the king of the screen, Singapore has become the only developed country in Southeast Asia with its geographical advantages, and Taiwan still has TSMC. Even Japan, which claims to be "lost for 30 years", has enjoyed a good time through the great industrial transfer of the United States in the 1950s. Even now, it can ".
Not to mention the participants in the second and third global industrial transfers. Japan, Germany, South Korea, and Singapore have all become developed countries; not to mention that the market is not large enough, and the preferential treatment of Hong Kong capital in the Mainland is not a legend; not to mention that the system is limited, one country, two systems, What else do you want?
But even so, a good card is still played to pieces.
Compared with the thriving Shenzhen, Hong Kong is very late.
How can this be called Hong Kong, the former "Pearl of the Orient?
Of course, our topic today is not politics, and ordinary people are not suitable to talk about politics; it is just that people with a little common sense know that most of the current international disputes directly or indirectly point to the United States, and in the "trade war" that started in 2018 We cannot "be alone".
This is not a speculation. Under the "sinister intentions" that foreign media are too lazy to cover up, in this 5G war in which Trump has made bold words to ensure that the United States will win. Hong Kong has become another pawn after the great powers relay Taiwan.
Why is 5G so important?
On the one hand, readers who have read the previous article "5G era, the opportunities and hidden dangers behind the Internet of Everything?" "4G changes life, 5G changes society" is really not a slogan.
This has brought great uncertainty to Apple, Qualcomm, Google and Facebook, a group of Internet giants entrenched at the top of the food chain.
On the other hand, the United States, which has tasted the benefits of huge profits from technology, will naturally not tolerate challengers shaking its position: from the "national security theory" concocted by SIA (Silicon Valley Semiconductor Industry Association) in 1985 to Alstom's "American Trap" in 2015; From ZTE's 7-year ban in 2018 to Meng Wanzhou's arrest in December 2018; The "long arm jurisdiction" hand of the United States is too long.
However, ZTE is not a Japanese semiconductor 30 years ago, and Huawei is not Alstom in 2013. Although ZTE lost, it was enough to alert the Chinese people. Huawei did not win, but resisted all kinds of pressure from the United States by itself.
It is Huawei's "one-man" momentum that gives the Chinese government more energy to "deal with" the US trade war. This is a war that we cannot afford to lose in the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
5G is naturally not so easy to be banned. Even the position of the Five Eyes Alliance is not firm enough in the face of social development trends. In addition, Huawei's equipment is advanced and cheap, and Americans even did not want to recognize Huawei's patents at one time.
However, the "aggressiveness" of the United States is not useless. At least, it exposes our weaknesses on chips and systems. Although both of them are double-edged swords of "hurting one thousand enemies and damaging eight hundred", they can't resist the pain of killing people!
Although we can't do without the United States and the United States can't do without us in a highly divided social division of labor, the two are not equal; we need American technology, but what the United States is jealous of is only our market. Once people give up their love, the Internet economy built on overseas high technology is like water without a source.
This is not over yet, imposing tariffs, cutting interest rates by the Federal Reserve, listing China as a "currency manipulator" and withdrawing from the Intermediate-Range-Range-Range Treaty ...... The United States is taking the world's economic structure and political security into the water.
In the process of "fishing in troubled waters", there is no doubt about the strength of the United States, and it is necessary for us to be sober and no longer have any superfluous illusions about the United States.
Because on top of that little chip:
Technology is not only productivity, it is also the right to speak.
(1)
The Birth of Chip
○

Chip: chip, also known as integrated circuit; It is a way to miniaturize circuits (mainly including semiconductor equipment, but also passive components, etc.) and are often manufactured on the surface of semiconductor wafers.
This idea was first proposed in 1952 by Jeff Dammer of the Royal Radar Institute: to make transistors and other devices required for a circuit on a semiconductor.
But the value of this idea itself is limited, because we always lack a process that can realize it.
Until Texas Instruments and Fairchild came up with their own solutions.
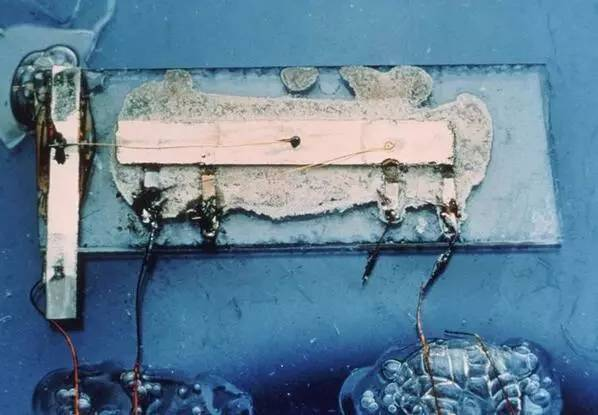
The first integrated circuit invented by Kilby
In September 1958, Texas Instruments (TI) engineer Kilby connected ten volts to the input terminal, and then connected an oscilloscope to the output terminal. At the moment of connection, the first integrated circuit made of a single material in the modern electronics industry was born.
Kilby's circuit is relatively primitive and rough, but its significance lies in proving the possibility of the idea of "integrated circuit/chip.
Although Kilby mentioned the relevant ideas in his diary as early as July 1958 and made many attempts, its related patents were "forced" out: the application for an integrated circuit patent submitted by the US Radio Corporation (RCA) in January 1959 made TI wake up quickly and successfully stopped the "solid micro electronic circuit" in March.
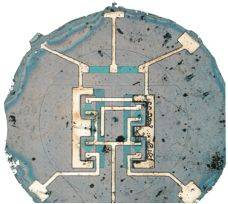
Fairchild's Silicon Crystal Integrated Circuit
Fairchild Nois also had a similar idea at the end of January 1959-based on Fairchild founder Honey's planar process and diffusion technology on silicon wafers, but it was not immediately developed until after TI's release. Fairchild used its own advantages to optimize TI's blind spot twice diffusion and wire interconnection, and applied for a patent in July.
Since then, TI and Fairchild have been fighting for the invention rights of integrated circuits.
In 1966, Kilby and Nois were awarded the "Ballantine" medal by the Franklin Society at the same time. Kilby was hailed as the "inventor of the first integrated circuit", and Nois was hailed as "proposed suitable for industrial production." The theory of integrated circuits.
The technologies of the two companies can be said to have the same root. Kilby directly studied under Bell Labs, and Shockley, the former employer of the Fairchild Gang of Eight, is one of the inventors of Bell Labs triode.
However, this kind of integrated circuit was not optimistic at the time, until two huge military engineering programs-the Apollo moon landing program and the militia missile development program promoted the development of integrated circuits.
1. Analog chip
In international semiconductor statistics, the semiconductor industry is divided into four categories: integrated circuits, discrete devices, sensors and optoelectronics.
If classified according to different processing signals, all integrated circuits are only analog chips and digital chips.
Such as TI and Fairchild, should be regarded as early analog chips; generally used in signal amplification and power supply, such as radio and speakers, charger power supply.
Analog chips are not developing fast due to their application scenarios and structural limitations, but have gained a "new life" after the introduction of digital circuits ".
2. Digital Chip
What we usually call chips belongs to digital chips, which can be roughly divided into memory chips and functional chips.
Memory chips are memory in the traditional sense. They were originally used to replace the heavy and expensive magnetic cores at that time. At first, they had a capacity of tens of hundreds of K. Now they have developed to tens of G and hundreds of G. Computers, mobile phones, U disks and memory cards are widely used, and the storage capacity has increased to millions of times.
Memory is divided into several categories: according to the structure is divided into magnetic core memory, semiconductor memory, disk, tape and so on, according to the relationship with the central processing machine can be divided into internal memory and external memory two categories.
However, it is often a peripheral device with a single function and is highly substitutable.
Functional chips are derived from different categories due to different structures and logic:
The rapid development is the CPU, which represents Intel's CPU. It has developed from the simplest 4-bit to the 64-bit 8-core Core i7. The development speed is amazing.
In the process of Intel and AMD falling in love and killing each other, it also breeds the use of GPU as the foundation of its body. This kind of GPU is specially designed to perform complex mathematical and geometric calculations. It can provide tens or even hundreds of times the performance of CPU in some calculations such as floating-point operations and parallel calculations.
Different from the CPU and GPU based on von Neumann structure, FPGA (field programmable logic gate array: its internal computing relationship can be easily changed through code, and the signal processing speed is very fast) has a tendency to replace CPU and GPU as the next generation processor.
With the development of mobile Internet, mobile phones have gradually derived image sensors and RF chips:
Early image sensors use CCD technology, which belongs to an analog chip, so it limits its integration level, it is difficult to improve pixels, and the cost is high; the current CMOS technology greatly improves the integration level, which has tens of millions of pixels on mobile phones.
In recent decades, the further development of wireless communications such as mobile phones and WIFI once again gave birth to radio frequency technology; the difficulty of this chip is not in integration, but in materials and manufacturing processes.
Application specific integrated circuits Netronome by fabless semiconductor companies
The recently popular AIOT chip, or AI chip:
In addition to the above GPU,FPGA is a general-purpose chip;
There are also ASIC chips designed for customized AI products or services, mainly focusing on accelerating machine learning;
There is also a neuromorphological computing chip inspired by biological brain. They are designed based on neuromorphological architecture and represented by IBM Truenorth.
In this process, with the user's ultimate pursuit of chip algorithms, performance and efficiency, AI chips are developing in three directions:
1. Cloud expansion: convenient and compatible deployment;
2. Edge calculation: push efficiency to the extreme;
3, algorithm profile: real-time algorithm definition chip.
②
United States: Fairchild Gang of Eight
○

Above, we can roughly summarize the development of chip technology:
Chip = analog chip digital chip {memory chip function chip [CPU GPU FPGA (image sensor RF chip)]}
With the continuous development of chip technology, even once based on chip technology to establish a huge Internet world; from analog chips to digital chips, from functional chips to AI chips, human beings are no longer satisfied with giving them simple and repetitive work. We are still trying to empower their "subjective initiative.
In this process, although the inventor of integrated circuits is still controversial, the emergence of functional chips is understandable; and all this originated from a magical "heavenly group"-the Fairchild Gang of Eight.
In 1955, Shockley, the "father of transistors", established a semiconductor laboratory in Silicon Valley and brought silicon to Silicon Valley.
In 1956, Shockley Laboratory joined eight amazing scientists, they are: Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, Blanc, Claire, Herney, Rast, Roberts and Grinik.
Although Shockley's arrival marks a new era in the electronics industry in Silicon Valley, the birth of Silicon Valley is marked by the establishment of Fairchild Semiconductor Company: In 1957, the Fairchild family invested 1.5 million US dollars, including Kleiner. Seven scientists, together with Noyce, who joined halfway, fled Shockley Laboratory and established Fairchild Semiconductor Company.
Fairchildren's significance to Silicon Valley is just like Bauhaus's significance to industrial design. They ignited the fire of innovation in Silicon Valley.
The accumulation of technology on the triode has successfully brought the Fairchild Eight Gang to a new field, and the invention of integrated circuits is the spark of their personal talents and technical barriers.
Although it crashed with Kilby's integrated circuit during this period, Fairchild missed the honor of being the first person in integrated circuits, but the two schemes are inherently complementary to each other at some level. As for the quality of RCA's integrated circuits, I am a little curious?
From Shockley to Fairchild, the experience of studying in the laboratory and growing up in Fairchild has a sense of mission, especially their achievements after they run away again.
In 1968, two employees of Fairchild Semiconductor, Noyce and Moore, left together, and took the craft expert Grove along the way to start Intel.
In 1969, Sanders, the successor of Valentine, the vice president of sales of Fairchild Semiconductor, and the head of sales, left and took seven colleagues to start AMD, which became the former boss Noyce and Moore founded Intel. Long-term opponent.
In November 1971, the world's first personal microprocessor Intel 4004 was born. For the first time, the functional units necessary for programmable computers were integrated on a single chip, which triggered a technological revolution in the chip industry.
Interestingly, just as Fairchild integrated circuit was forced out by Kilby, Intel 4004 is not Intel's original goal, but a list of customized chips Busicom by a Japanese calculator company: Intel engineers think that Busicom system composed of 12 integrated circuits is too complicated and innovatively concentrates computing units on one chip.
This is the emergence of CPU, the crown pearl of today's semiconductor industry.
The difference of founders determines the different genes of Intel and AMD. For more than 20 years, "love and kill each other" has been at odds. AMD with weak technology has been dragged through the most advanced 386 technology era by Intel.
It was also here that small transparent Avida, born in 1993, found an opportunity to transform GPU. When AMD staged a Jedi counterattack under the leadership of new CEO Lisa Su in 2014, Intel's housekeeping ability Moore's Law came to a dead end. At this moment, Avida has become the overlord of GPU.
In November 2017, in order to suppress the "enemy of the enemy" Nvidia, Intel and AMD even announced an alliance; but within a few days of the alliance announcement, Intel poached one of AMD's core technology leaders and graphics executives. Even the melon eaters were caught off guard.
The latest news is that Apple spent 1 billion US dollars to buy Intel's baseband chip business and gamble on the 5G market.
As for how did Fairchild go after the Fairchild Gang of Eight left?
In 1979, it was sold to a French oil company, Schlumberger.
After that, Fairchild was resold, resurrected, and independent, and finally acquired by Anselme in 2016; since then, there has been no Fairchild in the world.
(3)
Japan: Big ups and downs
○

We must not worry about Intel's ups and downs, but selling its baseband business for $1 billion will surely make neighboring countries feel sad.
After all, Intel 4004 was originally produced by Intel Busicom, and the latter "practiced" with its own project. Although Intel finally bought back the ownership of Intel 4004 from Busicom for $60000.
If Busicom saw the value of Intel 4004 earlier, but history did not.
However, the development of integrated circuits in Japan is still inseparable from the "aid" of the United States:
First: After World War II, the Japanese had a strong sense of purpose, and they urgently needed a revival in the wasteland after the war;
Second: After the outbreak of the Korean War in 1950, the United States began to support Japan, and Japan successively introduced the latest transistor and integrated circuit technology from the United States at low prices;
In 1953, Tokyo Communications Engineering Co., Ltd. (renamed Sony in 1955) introduced the patent license of transistor from Westinghouse Electric (AT&T subsidiary, Bell Company is the predecessor of AT&T) at a low price of 9 million yen.
In 1962, Nippon Electric Co., Ltd. (NEC) purchased the planar lithography production process from Fairchild Semiconductor Company of the United States.
During the same period, Hitachi signed technology transfer agreements with RCA, General Electric and Toshiba.
In 1968, Sony and Texas Instruments established a joint venture in Japan with 50% shares.
It is precisely because of the "import" of a large number of core technologies in the United States that the industry has quickly filled the gap and made great progress in technology.
In addition, in the 1970s, with the help of Japan's "government, learning and research" integrated national model, VLSI plan made Japan's semiconductor industry soar rapidly, and finally became the winner of the first "industrial transfer" in the history of semiconductors in the 1980s, winning the monopoly position of the memory market.
Different from the professional chip companies in the United States, it is popular in Japan that the whole machine and chip are one company. Their own whole machine uses their own chips, and their own chip companies provide support for their own whole machine, which promotes the rapid development of the chip industry.
However, after the US-Soviet hegemony came to an end, the United States quickly freed up its hand to shift its strategic focus to Japan. With the signing of a series of treaties such as the Plaza Accord and the Semiconductor Agreement, Japan quickly entered the bubble economy in the late 80 s. In addition, the rigidity of its own system did not catch up with the trend change of semiconductors, missed the great development of personal PC, and still failed to catch up with the subsequent wave of mobile.
Many people think that this US-Japan semiconductor war has caused Japan to lose 30 years and completely lose its own future; but the reality is that Japan has lost, but it is not as embarrassed as imagined:
Although Japan lost to the United States, it still has a place in the "Warring States Seven Heroes" of memory chips (American Spansion, SanDisk, Micron, Kingston; South Korea's Samsung, Hynix; Japan's Toshiba).
In the field of CMOS sensors that emerged from mobile phones, Japan is still the main player.
Japanese Renesas also have a say in RF chips.
Even now, Japan is still deeply rooted in the semiconductor industry:
Japan accounted for 7 of the world's top 15 semiconductor manufacturers in 2018;
Especially from the perspective of the entire semiconductor industry chain, Japan has more than 50% of the 14 important semiconductor materials and is the world's largest exporter of semiconductor materials;
In recent years, Japan has also made efforts in the fields of autonomous driving chips, Internet of things chips and robot chips, winning a leading position in the world market.
This is not, 2019 Japan just got serious:
In July, the Ministry of Economic and Trade Affairs announced that it would restrict the export of three semiconductor materials for the manufacture of televisions and smartphones to South Korea;
In August, the new version of the "Export Trade Management Order" was passed to remove South Korea from the "whitelist countries" that have set preferential treatment in security export management, which scared South Korea.
It can be seen that people's forbearance is not a little bit.
④
South Korea: Government Consortium
○

The origin of semiconductors in South Korea dates back to 1959.
That year, LG's predecessor, "Venus Club", developed and produced South Korea's first vacuum tube radio; although South Korea at that time did not have the ability to produce independently, it could only assemble imported components.
Thereafter:
In the 1960s, South Korea was once the "foundry" of American Fairchild and Motorola ";
In the 1970s, South Korea became the "private land" of Japanese Sanyo and Toshiba ".
Until the 1980s, the development of South Korea's semiconductor industry was still limited, just an assembly node for cheap labor.
But after Park Chung-hee came to power, the government began to release amazing "specials" to entrepreneurs ".
In 1975, the Korean government announced a six-year plan to support the semiconductor industry; the Korean government also organized a "government-civilian integration" DRAM joint development project, that is, through government investment to develop the DRAM industry.
In 1982, the Korean government issued the Semiconductor Industry Support Plan and the Semiconductor Support Specific Plan; however, private enterprises did not follow the government's pace, but introduced technology and equipment to focus on the production of DRAM (dynamic random access memory).
In 1985, South Korea passed the "Industrial Development Act", emphasizing the role of the market and reducing government intervention in the market.
In the process, the South Korean government even privatized large aviation, steel and other giants and allocated them to large consortia.
Finally, Samsung gradually narrowed the gap from 64K DRAM to 16M DRAM through simultaneous research and development of two teams at home and abroad through the horse racing mechanism, gradually narrowing the gap from 5 years to 3 months. Finally, Samsung's market share exceeded 50% in 1993 and 256M DRAM became the market leader in 1994.
It took Samsung only 11 years from 1983 announcing its entry into the semiconductor industry to standing at the top of the DRAM market in 1994.
Although South Korea did not acquire core technology from the United States and Japan in the 60/70 s, it at least completed the early education of the market. After that, Samsung acquired the "original shares" of technology from Sharp in the United States and Japan in 1983 ":
I bought the design technology of 64K DRAM from Micron, which is difficult to operate;
The key processing technology-MOS technology was introduced from Sharp Corporation of Japan.
In addition, Samsung has also obtained a license agreement for Sharp's "complementary metal oxide semiconductor process.
Of course, Samsung is only a microcosm of the rise of South Korea's semiconductor industry. Besides Samsung, companies such as Venus (later LG) and Hyundai (later renamed Hynix Semiconductor and acquired by SK Group) "copied" the Japanese semiconductor industry model (Li Bingzhe went to Japan many times to visit teachers), rapid transition from simple assembly production to precision wafer processing production and into the era of large-scale integration (VLSI) production.
Subsequently, Samsung took advantage of the bursting of Japan's economic bubble, Toshiba, NEC and other giants significantly reduced the timing of semiconductor investment and increased investment in the introduction of Japanese technicians; this laid the foundation for Samsung to surpass Japan's NEC to become the world's largest DRAM manufacturer.
After 1995, Samsung launched a number of "counter-cyclical law" price wars, making most of the DRAM field manufacturers go bankrupt, and gradually formed the DRAM field only a few monopoly market status quo.
In 2017, Samsung once squeezed Intel into the leading position in global semiconductor revenue, ending Intel's 25 consecutive years of "the world's largest factory" since 1992.
However, with the great development of PC personal terminals, Moore's Law has become popular, users' requirements for product update iteration efficiency have been further improved, and the design and manufacturing of semiconductors have begun to divide labor. Two modes of Foundry and IP authorization have emerged. Some IC design companies such as Qualcomm, Cyrus and Avida have emerged in the United States, while a number of pure contract manufacturing companies such as TSMC, Lianhua and Lijing have emerged in Taiwan.
South Korean companies have also been greatly impacted. Only Samsung is still large and complete. Venus has become LG's focus on display screens, while modern chip companies have separated and become independent chip companies.
⑤
TSMC + ARM + Qualcomm
○

In the process of the rise of Korean semiconductors, the global semiconductor industry has also undergone a large-scale division of labor:
Established in 1987, TSMC created a Foundry model, that is, a wafer generation factory that only produces chips;
Acorn, which was renamed ARM in 1990, was jointly funded by Apple and chip manufacturer VLSI to create an IP authorization model.
This division of labor has shattered Intel's "vertical integration" model, with downstream manufacturing and upstream IP research and development and design in the semiconductor industry divided into separate industries.
If TSMC is only a sign of the maturity of South Korea's "foundry" in the 60/70 s, the emergence of ARM "does not produce chips by itself, but only licenses IP cores to other companies" has completely shaken the past industry pattern. They have greatly lowered the entry threshold for the semiconductor industry.
As ARM and TSMC have assumed the maturity of the working mode of one end of the industrial chain, the "chip design" link in the middle has gradually developed into an independent track-Fabless manufacturers that do not do production, do not need to rebuild factories or do bottom-level research and development. This led to the rise of Avida and Qualcomm's prosperity (Qualcomm was founded in 1985 and only started selling chips in 1994).
ARM, which occupies the 95% market on the mobile side, gradually competes with Intel, the dominant player on the CPU, forming the two lowest standards for semiconductor production in the world.
With the addition of new semiconductor players, TSMC's technological level has surpassed that of traditional vertical manufacturers Intel and IBM in recent years, occupying more than 50% of the market share and leading the world in the latest 5nm process.
As the "IP authorization + Fabless + Foundry" mode reduces the overall cost of mobile phone chips, domestic mobile phones can "let a hundred flowers blossom" and gain a firm foothold in the "full screen campaign.
Qualcomm, on the other hand, is gradually exposing the drawbacks of its high royalties.
With Huawei and Samsung self-developed 5G SOC and Apple's acquisition of Intel's baseband business, Qualcomm's monopoly is bound to be shaken.
In this process, Qualcomm lost more than just its right to speak. With the emergence of more MediaTek-Xiaomi, Qualcomm suffered from both sides.
⑥
Times Call China Core
○

In the 50s of 2050s, anyone who was willing to spend 25,000 US dollars could buy AT&T's patent to license the production of transistor.
In 1971, Intel bought back the future of Intel 4004(CPU) from Busicom for only 60,000 US dollars.
In the 1980s, South Korea faced a situation where technology could be bought, and it just caught up with the U.S. sanctions on the Japanese semiconductor industry; the spillover of technology and talent accelerated the rise of the Korean semiconductor industry.
What is the situation in China?
In 1957, when eight talents less than 30 left Shockley to form Fairchild Semiconductor, Huang Kun and Xie Xide, the two originators of semiconductors in China, compiled the first book "Semiconductor Physics" in China. Senior Lin Lanying had just returned from the United States.
In 1959, China successfully pulled out silicon single crystals. At this time, Fairchild Semiconductor received an order from the US Department of Defense and produced the first integrated circuit.
However, China did not have its first integrated circuit until 1965. At this time, the price of Fairchild integrated circuit has dropped to one dollar.
X86 was born in 1978, and we began to reform and open up.
The rise of Japanese semiconductors was completed in the process of technology import from the United States and concentrated on tackling key problems. The rise of South Korea's semiconductors was completed with the support of the government from the United States and Japan. TSMC, ARM and even Qualcomm have just caught up with the great era of division of labor and fission Fabless in semiconductor design and manufacturing.
However, China had almost no "core" in the half century before ZTE was founded.
However, we need to break through the blockade of 1952 Batumi and 1996 Vanathan first, and then the US will block ZTE and Huawei. In this process, Intel in the PC era does not need to count on it. Even ARM in the mobile era has chosen to stand on the sidelines. All we can count on is to break through in the AIOT era.
The United States earns more than $200 billion a deficit in China through semiconductors every year.
China's semiconductor industry has just shown a little "upward" in the field of mobile communications, and the United States is busy "obliterating".
In March 2017, the U.S. Department of Commerce imposed the strictest export restrictions on ZTE in U.S. history: ZTE was forced to compromise with the U.S. government and had to pay a fine of nearly $1.2 billion.
In 2018, the United States directly imposed a 7-year ban on ZTE.
After the ZTE incident, the United States smeared Huawei as a daily operation and even used its allies to threaten them not to use Huawei's network equipment.
However, this is only a small matter. On May 15, US President Trump signed an executive order to add Huawei to the list of "export embargo" entities. On May 22, ARM also announced the suspension of chip architecture cooperation with Huawei.
And Haisi, Huawei was born in this "extreme survival" environment.
Even if people with core are like this, what will happen to OPPO, vivo and Xiaomi without heart?
Even if Qualcomm is still willing to send high chips to Chinese mobile phones, the U.S. government is only a symbolic fine. The same model of processor, the same set of mature solutions in the industrial chain, the same under-screen fingerprint or water drop screen design will certainly bring them into the quagmire of homogenization.
Although Xiaomi grabbed half of the tickets for the world's top 500 and held hands with MediaTek, Xiaomi did not have much capital to have a showdown with Qualcomm because of the core technology layout of 5G.
However, with the further development of AIOT, Huawei, Samsung and Apple are likely to become the "new three poles" at the top of the industrial chain in the Internet of Everything era ".
⑦
China Core Power
○

After 2000, most excellent Chinese chip companies were established at this stage of time, while foreign countries entered the Fabless stage as early as the 1990 s. It can be seen that we are behind more than 30 years, and we are behind an era.
At this moment, we are trapped by the wave of Internet economy. The rapid development of Internet economy has occupied too much attention of users. From Tencent to Ali, from microblog to WeChat, from fast hand to tremolo... The rapid expansion of domestic Internet economy once compressed the living space of traditional industries.
If it were not blocked, I believe everyone would not know ZTE as a company.
Initially run by TSMC, Zhang Rujing led 400 chip engineers from Taipei to Shanghai in 2000 to establish SMIC.
Coincidentally, Zhang Rujing's former boss was Kilby, who developed the world's first integrated circuit.
It was not until the emergence of Huawei that we realized that made in China could be so powerful.
However, domestic Internet companies are not standing idly by for the high-tech industry:
In 2016, the "big men" of China's Internet industry, including Ma Huateng, Li Yanhong, Ding Lei and Xu Xiaoping, donated the "Future Science Award" with a single prize of US $1 million and promised to donate for 10 consecutive years.
In 2018, on the occasion of the 20th anniversary of Tencent's establishment, Tencent Foundation announced that it would invest 1 billion yuan of start-up funds to fund the establishment of the "Science Exploration Award".
And with the rise of Chinese mobile phone brands, chips have also received more extensive attention:
In 2009, Huawei launched a K3 processor water test smartphone, which is also the first smartphone processor in China.
In 2016, Cambrian released the world's first commercial deep learning dedicated processor IP-Cambrian 1A processor for smart phones, security monitoring, drones, wearable devices and smart driving devices.
In February 2017, Xiaomi held a "my heart surging" conference in Beijing, officially releasing the independent core "surging S1".
In July 2018, the most eye-catching release at the Baidu AI Developer Conference was China's first cloud-based full-featured AI chip "Kunlun" independently developed by Baidu ".
In January 2019, Huawei released two 5G chips-Tiangang and Balong 5000 (Balong 5000).
In July 2019, at Baidu Create 2019 Baidu AI Developer Conference, Baidu and Huawei jointly released the far-field voice interaction chip "Honghu".
In July 2019, Ali Pingtou brought Xuantie 910 in the name of sword weapon.
In July 2019, Glory released Glory 9X mobile phone in Xi 'an. This Glory mid-range flagship caused a stir in the market because it was equipped with Kirin 810 processor, which can suppress Qualcomm's mid-range flagship 730.
In July 2019, MediaTek released a chip named "Game Born", code-named G90.
In August 2019, Tsinghua University developed the world's first heterogeneous fusion brain-like computing chip-"Sky Movement". The "driverless bicycle" driven by this chip was once on the cover of the latest issue of Nature!
The combination of mythology, mythical beast and Excalibur chip really has the color of Chinese national romanticism.
Among them: day movement 28nm process, Kunlun 14nm process, Xuan iron 910 12nm process.
At present, the chips with 7nm process include Kirin 980, Kirin 810, A12 and Qualcomm Xiaolong 855/855. The 7nm 5G chip has a few Balon 5000, MediaTek M70 and Xiaolong X55.
TSMC has trial-produced 5nm process chips, and Samsung has also announced its own contract manufacturing plan: 5nm will be rolled out within this year, mass production in the first half of next year, 4nm will be designed within this year and mass production in 2021.
Whether it is Intel's 7nm, TSMC's 5nm or Samsung's 4nm, we seem to have seen the ceiling of lithography technology. Now the most advanced manufacturing process is approaching the limit, but the next wave of chip technology is still invisible, and it is very likely to complete the iteration in the era of Internet of Everything.
And that's what U.S. chip companies are anxious about.

Such a large chip history is a "dream country" built by mankind on the sand, and it is also the ultimate pursuit of mankind for integrated circuit technology:
If the discovery of integrated circuit technology in the United States is a godsend, then the rise of Japanese semiconductors is a tall building on the shoulders of giants.
If the rise of Korean semiconductors has the connivance of the United States and Japan's achievements, and more importantly, their control of the trend, then TSMC and ARM have accurately grasped the pulse of the times.
And China's semiconductor into the market, failure also market.
Our huge market makes countless high-tech companies want to come in, but they do not want to go. This certainly gives us room for the development of technology companies, but it will not easily allow us to cross boundaries.
This is the real core value of science and technology, and the right to speak in industry is its killer.
The United States must feel the threat of Huawei. Huawei is eroding its industrial discourse power and monopoly on standards, which makes the high-tech enterprises living in the "greenhouse" of the United States angry.
And this war has also spread from the Internet to reality, and from chips to systems. Now let's see if Huawei can break the ecological barriers of Android system?
Hongmeng, crucial.
PS: Some materials come from @ Tiger Smell @ Zhihu @ CSDN
The copyright of this work belongs to 何鲸洛. No use is allowed without explicit permission from owner.

New user?Create an account
Log In Reset your password.
Account existed?Log In
Read and agree to the User Agreement Terms of Use.

Please enter your email to reset your password
Excellent
Excellent
Can the national flag be used directly?
Yes, haowen
Wake up ~ ~ wake up ~ ~
Great!!!
This history is very cool
Praise the Chinese
Boss, why is this article so 6
There is a boiling momentum